How to understand UAE E-Invoicing Data Dictionary (Step by step)
UAE E-Invoicing Data Dictionary Guide: Understand PINT-AE requirements, mandatory fields, invoice types, and use cases for FTA compliance. Get your business ready.

Table of Contents
Hey there! Have you heard about the UAE's new e-invoicing rules? It might sound like a big, confusing puzzle.
Don't worry! The UAE Ministry of Finance has released the full rulebook called the E-Invoicing Data Dictionary (PINT-AE), and this easy blog will explain it in simple words.
What is the E-Invoicing Data Dictionary in UAE?
Data Dictionary is the official rulebook that every business in the UAE must follow when creating e-invoices. It's like the instruction manual for the entire country that ensures every invoice speaks the same digital language.
This master guide tells businesses exactly what information to include, how to format it, and when it's required.
- All e-invoices follow the same clear structure
- Invoices can be exchanged between different companies seamlessly
- The tax authority's systems can process and verify them automatically
What Does a Data Dictionary Entry Look Like?
The data dictionary isn't just a list of field names. For every single piece of information that could go on an invoice, the dictionary provides a detailed description, its format, and the rules for using it.
Let's take a very common field as an example: Invoice Issue Date.
The data dictionary doesn't just say "include the date." It gives precise, unambiguous instructions like this:
| Field Name (Code) | Description | Format & Data Type | Business Rules & Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT-2: Invoice Issue Date | The date when the invoice was issued. | Format: YYYY-MM-DD Data Type: Date | • Mandatory, must be included on every invoice • Cannot be a future date • Must be the actual date of issue, not the date of supply or payment |
Why is this level of detail so important?
Imagine one company writes the date as April 25, 2024, another uses 25/04/24 (DD/MM/YYYY), and a third uses 04/25/2024(MM/DD/YYYY). A computer would see these as three completely different things! This would cause errors and rejections.
The data dictionary solves this by mandating the international standard format 2024-04-25. This ensures every system, in every company, reads and interprets the date in exactly the same way.
This same rigorous definition is applied to every field, from the invoice total to the smallest line item on an order, creating a universal language for business that is clear to both humans and machines.
Free up your tax team to focus on core strategic work while Complyance ensures 100% compliant, rejection-free invoicing. Complyance is an Accredited Service Provider under the UAE e-invoicing framework, enabling structured, secure invoice transmission aligned with the official PINT-AE Data Dictionary.
Understanding the Types of Fields and Invoices
Fields in the UAE e-invoicing framework are created based on specific business rules and compliance requirements.
Each field serves a distinct purpose and falls into one of three categories, ensuring clarity and standardization across all transactions.
- Mandatory - Must be included
- Optional - Can be added for extra detail
- Conditional - Required only in specific situations
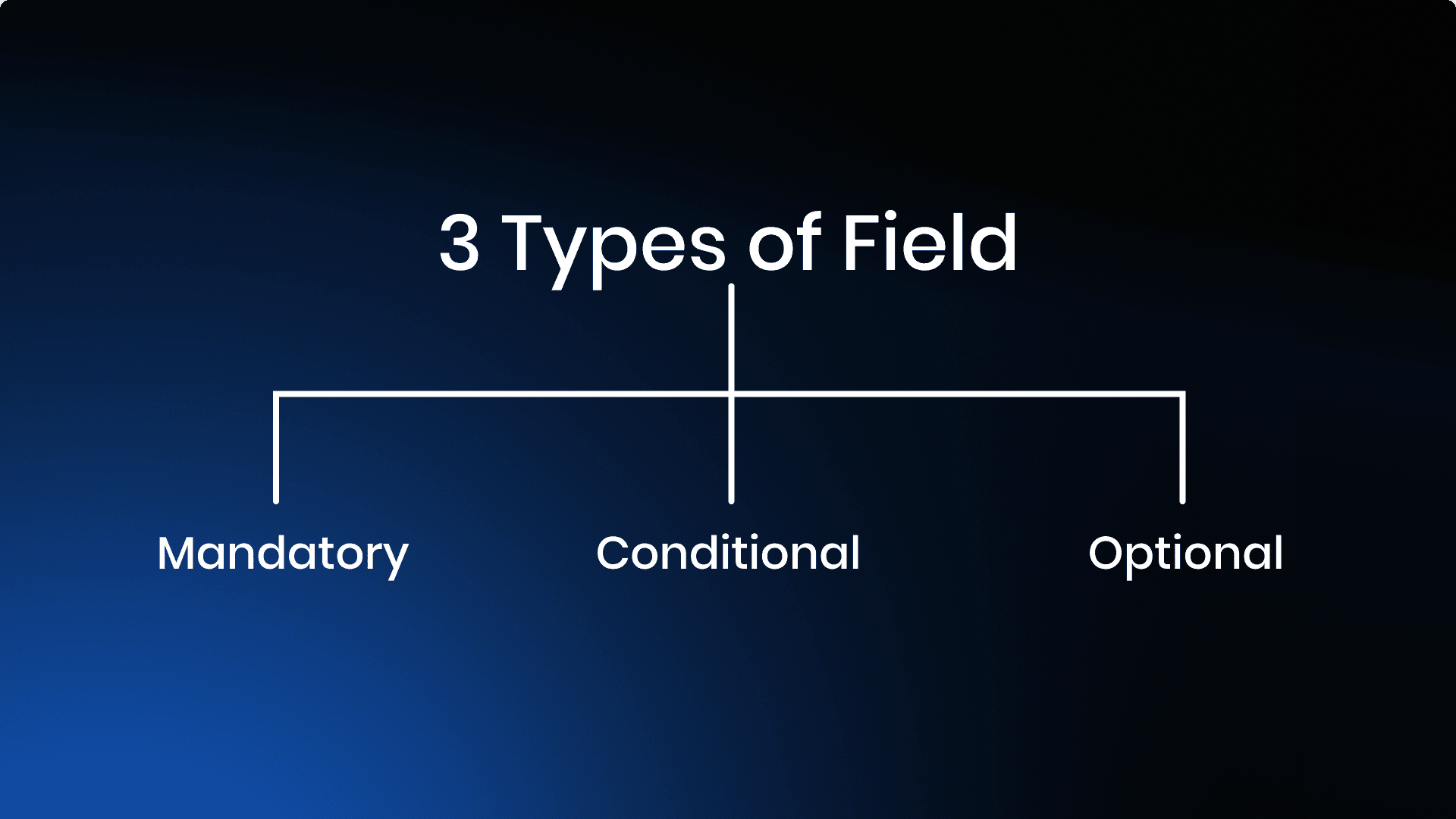
1. Mandatory Fields
These fields are essential for every invoice and must be included without exception. They form the foundation of a compliant e-invoice, and omitting any of these will result in rejection by the tax authority.
Examples include:
- Invoice number (BT-1)
- Invoice issue date (BT-2)
- Seller's Tax Registration Number (TRN)
- Total amount with tax
2. Optional Fields
Optional fields provide additional context or details but are not required for validity. Businesses can include them to enhance clarity or support specific operational needs.
Examples include:
- Purchase order number
- Invoice notes
- Detailed item descriptions
3. Conditional Fields
These fields are required only under specific circumstances defined by business rules. Their inclusion depends on the nature of the transaction, such as cross-border trade or reverse charge scenarios.
Examples include:
- Reverse charge note
- Export reason code
Two Main Invoice Types
The fields are organized into two primary invoice types, each serving different transactional needs:
Standard Tax Invoice
- Used for taxable B2B supplies
- Requires all mandatory fields, including a full VAT breakdown
- 50 mandatory fields
Simplified/Commercial Invoice
- Used for exempt supplies or B2C transactions
- Requires slightly fewer mandatory fields
- 49 mandatory fields
This structured approach ensures every invoice meets compliance requirements while maintaining flexibility for different business scenarios.
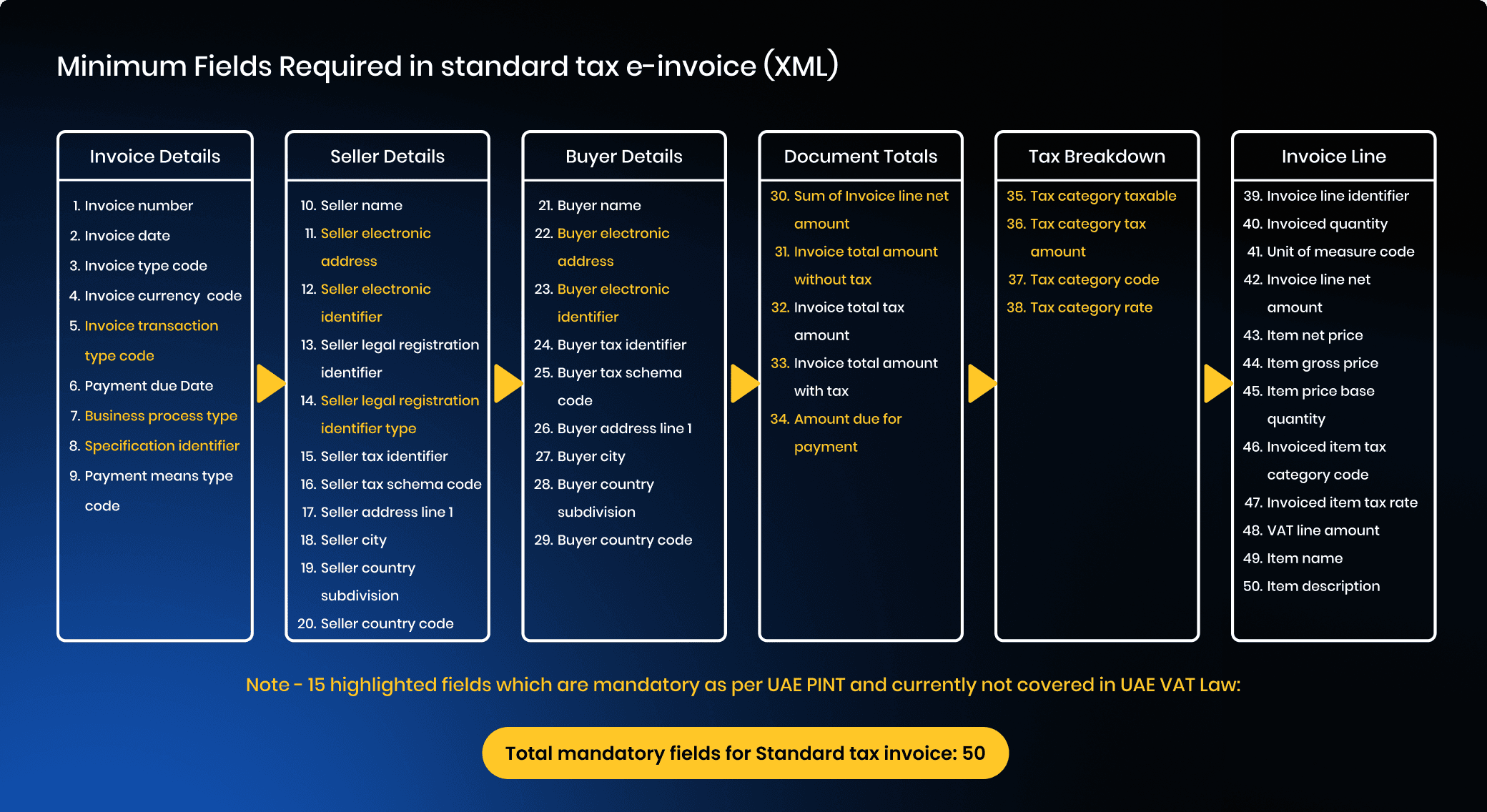
Invoice Details
| No. | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Invoice Number | Unique identifier assigned to the invoice. |
| 2 | Invoice Date | The date the invoice was issued. |
| 3 | Invoice Type Code | Identifies type (standard, credit note, debit note). |
| 4 | Invoice Currency Code | Currency used for the invoice (ISO code). |
| 5 | Invoice Transaction Type Code | Defines the nature of the transaction. |
| 6 | Payment Due Date | Deadline by which payment must be made. |
| 7 | Business Process Type | Indicates the type of business transaction. |
| 8 | Specification Identifier | Confirms compliance with PINT-AE standard. |
| 9 | Payment Means Type Code | Specifies method of payment (e.g., card, bank transfer). |
Seller Details
| No. | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Seller Name | Registered legal name of the supplier. |
| 11 | Seller Electronic Address | Digital address for e-invoicing communication. |
| 12 | Seller Electronic Identifier | Unique electronic identifier for the seller. |
| 13 | Seller Legal Registration Identifier | Official trade license or registration ID. |
| 14 | Seller Legal Registration Identifier Type | Type of registration (e.g., Trade License, Emirates ID). |
| 15 | Seller Tax Scheme Code | VAT scheme under which seller is registered. |
| 17 | Seller Address Line 1 | Primary address of the seller. |
| 18 | Seller City | City where the supplier operates. |
| 19 | Seller Country Subdivision | Emirate or region of the supplier. |
| 20 | Seller Country Code | Country code in ISO format (e.g., AE). |
Buyer Details
| No. | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 21 | Buyer Name | Registered legal name of the buyer. |
| 22 | Buyer Electronic Address | Buyer’s digital e-invoicing address. |
| 23 | Buyer Electronic Identifier | Unique electronic identifier for the buyer. |
| 24 | Buyer Tax Identifier | VAT registration number of the buyer. |
| 25 | Buyer Tax Scheme Code | VAT scheme applicable to the buyer. |
| 26 | Buyer Address Line 1 | Primary address of the buyer. |
| 27 | Buyer City | City of the buyer’s business location. |
| 28 | Buyer Country Subdivision | Region or emirate of the buyer. |
| 29 | Buyer Country Code | Buyer’s country in ISO format. |
Document Totals
| No. | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | Sum of Invoice Line Net Amount | Total before applying taxes. |
| 31 | Invoice Total Amount Without Tax | Full invoice value excluding VAT. |
| 32 | Invoice Total Tax Amount | Total VAT applied on the invoice. |
| 33 | Invoice Total Amount With Tax | Grand total including VAT. |
| 34 | Amount Due for Payment | Net amount payable after adjustments. |
Tax Breakdown
| No. | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | Tax Category Taxable Amount | Value used as the base for VAT. |
| 36 | Tax Category Tax Amount | VAT amount calculated per category. |
| 37 | Tax Category Code | Identifies type of tax (standard, exempt, zero-rated). |
| 38 | Tax Category Rate | Applicable VAT percentage (e.g., 5%). |
Invoice line
| No. | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 39 | Invoice Line Identifier | Sequential number for each line item. |
| 40 | Invoiced Quantity | Quantity of goods or services supplied. |
| 41 | Unit of Measure Code | Unit type for the item (e.g., pcs, kg). |
| 42 | Invoice Line Net Amount | Value of line item excluding VAT. |
| 43 | Item Net Price | Price per unit without VAT. |
| 44 | Item Gross Price | Price per unit including VAT. |
| 45 | Item Price Base Quantity | Quantity reference used for pricing. |
| 46 | Invoiced Item Tax Category Code | Tax category applied to this item. |
| 47 | Invoiced Item Tax Rate | VAT rate applied to this item. |
| 48 | VAT Line Amount | VAT calculated per line item. |
| 49 | Item Name | Name of the product or service. |
| 50 | Item Description | Additional description of the product/service. |
The 16 Different Invoice Scenarios (Use Cases)
So far, we've talked about the rules for individual fields. But a real business doesn't just have one type of transaction. You might export goods, issue credit notes, work through an agent, or handle complex supply chains.
This is where Use Cases come in.
A "Use Case" is a specific business scenario that requires a slightly different set of rules in the e-invoice.
The UAE's Data Dictionary doesn't just define one standard invoice; it provides tailored guidelines for 16 different situations to ensure every type of transaction is covered accurately and compliantly.
Here’s a simple breakdown of each one and what's special about them.
| Use Case | What It Is |
|---|---|
| Standard Tax Invoice | The most common invoice for VAT-registered businesses. |
| Reverse Charge Mechanism | When the buyer, not the seller, pays the VAT to the FTA. |
| Zero Rated Supplies | For sales that have a 0% VAT rate, like certain exports or healthcare. |
| Deemed Supply | When a business gives goods/services for free or for personal use. |
| Disclosed Agent Billing | When an agent sells on behalf of a principal company. |
| Summary Invoice | A single invoice covering multiple supplies over a period (e.g., a month). |
| Continuous Supplies | For ongoing contracts (e.g., monthly retainers, subscriptions). |
| Free Zone Supply | For transactions involving a Free Zone. |
| E-Commerce Supply | For sales made through online platforms. |
| Exports | For goods or services supplied outside the UAE. |
| Margin Scheme | For second-hand goods, art, antiques where VAT is on the profit margin. |
| Standard Tax Credit Note | To cancel or adjust a previous standard invoice. |
| Disclosed Agent Credit Note | A credit note issued by an agent. |
| Commercial Invoice | For supplies that are out of scope of VAT or exempt (e.g., bare land, local passenger transport). |
| Self-Billing | When the buyer prepares the invoice on behalf of the seller. |
| Self-Billing Credit Note | A credit note under a self-billing arrangement. |
Authoritative Reference
This guide simplifies key ideas. For the full, enforceable specifications, please refer to the official UAE document.
You can access and download the official consultation document here:
UAE Ministry of Finance - E-Invoicing Consultation Paper & Data Dictionary
Conclusion: A Rulebook for the Future of Business
As the UAE embarks on its e-invoicing journey, the Data Dictionary is a pivotal milestone in the move toward digital tax compliance.
By focusing on:
✔ Standardization → every invoice follows the same rules
✔ Clarity → no ambiguity in what data must be reported
✔ Collaboration → feedback from businesses shapes the framework
…the UAE is laying the foundation for a transparent, efficient, and globally aligned tax ecosystem.
Talk to our experts at Complyance, we’ll walk you through the mandate, field requirements, and how to get your ERP ready.
Related posts
Frequently Asked Questions
No. The UAE e-invoicing mandate applies only to B2B and B2G transactions and does not cover B2C transactions.
The UAE e-invoicing PINT is a standardized international framework for electronic invoicing, known officially as the PEPPOL International Invoice (PINT), tailored specifically for the UAE's regulatory and business needs as part of the country's move toward mandatory e-invoicing in July 2026.
Yes. All businesses that are part of a B2B or B2G transaction must comply with UAE e-invoicing rules, even if they are not VAT registered.
The official format is PINT AE, a structured XML format based on Peppol BIS 3.0, customized to meet the UAE’s specific tax requirements.
Yes, Complyance is an ASP provider and is in the process of being accredited by the FTA in the UAE.
Yes, Complyance offers expert guidance on the UAE e-invoicing public consultation process. Our team helps businesses understand regulatory updates, implementation requirements, and compliance strategies aligned with the latest government guidelines.
For detailed support, schedule a consultation with our specialist
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get the latest compliance updates, e-invoicing news, and expert tips delivered to your inbox.
ABOUT COMPLYANCE
Empowering businesses to automate e-invoicing and stay compliant in 100+ countries. Our platform simplifies regulatory complexity for enterprises and fast-growing companies.








