Zatca E-invoicing Requirements
Ensure VAT compliance with Zatca's e-invoicing requirements. Follow simple steps to meet regulations effectively and streamline your business operations.

Table of Contents
Introduction
In Saudi Arabia, electronic invoicing (E-Invoicing) through ZATCA (Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority) is a big change for businesses. However, many business people still don't know what this means or what they need to do. If you're one of them, don't worry. This blog is here to clear up all your doubts and give you a clear understanding of ZATCA E-Invoicing. Whether you run a big company or a small business, this guide will help you understand and follow the new rules.
Zatca's Core Objective
Electronic invoicing is a way to stop using paper for bills and notes about changes in prices. Instead, it uses a digital method where these documents are sent and handled electronically between the person selling and the person buying.
The rules for electronic invoicing in Saudi Arabia should be understood along with several other important documents. These include the Unified VAT Agreement, the VAT Law that was published on 4/11/1438H and any changes to it, and the VAT Implementing Regulation. Also, there are other decisions related to electronic invoicing, like the one about the rules, needs, and technical details for making electronic invoicing work in Saudi Arabia
Who Needs to Use E-Invoicing?
In Saudi Arabia, e-invoicing isn't just an option; it's a requirement for certain groups. Understanding who falls under these rules is crucial:
- Mandatory for Taxable Residents: If you're a business or individual residing in the Kingdom and subject to taxation, e-invoicing is not just a choice—it's a must. This applies to all your transactions that legally require tax invoices. Additionally, you're obliged to issue electronic notes for specific cases outlined in the VAT Law and its implementing regulations.
- Third-Party Invoice Issuers: In some instances, a customer or a third party might issue a tax invoice on behalf of a taxable resident. This situation, governed by the amendment in the VAT Implementing Regulations from November 9, 2021, effective since December 4, 2021, also falls under the e-invoicing requirement.
- Exemption for Non-Residents: For those who don't reside in Saudi Arabia, breathe easy. You're not required to issue electronic invoices or notes for transactions or receipts that are subject to tax within the Kingdom.
Benefits of Using Electronic Invoices
E-invoicing is more than just digitizing paper invoices. It's about enhancing the entire transaction process between buyers and sellers. This electronic procedure offers numerous benefits:
- Reduced costs and human errors in invoicing.
- Enhanced digitization in the supply chain.
- Improved accounting and bookkeeping practices.
- Enriched business ecosystem fostering fair competition.
- Reduced hidden economy transactions and commercial concealment.
- Enhanced consumer experience and relationships.
- Increased compliance with tax obligations.
Requirements for Generating Electronic Invoices
Adopting e-invoicing doesn't mean the fundamental rules of invoicing have changed. The switch to digital is more about the format than the content:
General Requirements:
- Shift from manual invoicing to electronic systems/solutions for invoice generation.
- Include a QR code on tax invoices.
- Include an appropriate invoice title based on the type of tax invoice being generated.
- Include the VAT number of the buyer in the invoice if the buyer is VAT registered.
- Generate invoices in XML format.
Optional Features:(mandatory for phase 2)
- Implementing anti-tampering measures, such as cryptographic stamps or hashes, to enhance security.
- Adding technical features like using UUIDs (Universally Unique Identifiers) for identification purposes.
Integration with ZATCA Systems
- Integrating your invoicing system with the ZATCA (Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority) systems for seamless compliance with their regulations.
- Adhering to VAT Laws: The move to electronic formats doesn't alter the foundational requirements for issuing invoices, debit notes, or credit notes. As a business, you're expected to continue adhering strictly to the provisions of the VAT Law and its implementing regulations.
- Maintaining Standard Practices: The essence of what needs to be included in an invoice remains the same. E-invoicing requires the same diligence and attention to detail as traditional paper invoicing. The primary difference is the medium, not the message.
By understanding these aspects, businesses can navigate the e-invoicing landscape in Saudi Arabia more effectively and ensure compliance with the Zatca regulations.
Understanding Key Terms in Zatca's E-Invoicing Regulations
This section breaks down important terms and concepts to help you better understand Zatca's E-Invoicing rules.
Simplified Tax Invoice:
This is a simpler version of a tax invoice, often used in business-to-consumer dealings. It's generally for transactions under SAR 1,000 and doesn't usually include detailed buyer information. It can also be used in some business-to-business transactions.
Electronic Note:
These are digital versions of debit and credit notes that need to be created as per VAT Implementing Regulation. Just like with invoices, scanning or copying paper notes doesn’t make them electronic notes.
Debit Note:
Sellers issue debit notes to adjust the value of an original invoice or VAT amount upward.
Credit Note:
Sellers issue credit notes to refund buyers or correct errors in invoices. They follow the same format as the invoice they are related to.
E-Invoice Solution:
This is the approved system used for generating electronic invoices and notes. It must meet specific technical standards set by the regulations.
FATOORA Portal:
Zatca’s online platform where electronic invoice data is collected. It's used to manage cryptographic stamps and view solutions and devices.
Cryptographic Stamp:
A digital stamp that verifies the authenticity and integrity of electronic invoices and notes. It also confirms the identity of the issuer.
Cryptographic Stamp Identifier (CSID):
A unique identifier linking the E-Invoice Solution to a third party that confirms the identity of the invoice issuer.
UUID:
A unique 128-bit number generated by an algorithm, used to identify invoices uniquely.
QR Code:
A matrix barcode readable by scanners or smart devices, used for validating electronic invoices and notes.
Hash:
A function that maps data to fixed-size values, ensuring that data hasn’t been altered. It's crucial for data integrity.
Invoice Reference Number:
A unique number identifying each issued invoice, as per VAT regulations. There's no fixed format for these numbers.
Clearance:
The process where the Authority checks that electronic tax invoices meet the required standards. They then stamp the approved invoices and notes.
Reporting of Simplified Tax Invoices:
This involves sharing simplified tax invoices and related notes with the Authority within 24 hours of issuance.
Human Readable Format:
The format of an invoice that can be easily read and understood by people, including buyers and the Authority.
The Authority’s Toolkit:
Testing tools provided by the Authority to ensure that invoices generated by businesses comply with the regulations and can be validated by the FATOORA Portal.
Tax Invoice:
A tax invoice is an official document issued by a seller to a buyer. It contains important details of a transaction, such as the items or services sold, quantities, prices, the total amount payable, and tax amounts. It's an essential record for both accounting and tax purposes.
Phase 1: Setting the Foundation (Generation Phase)
- Started: December 4, 2021.
- Main Goal: Businesses had to start using computers or electronic systems to create and keep their sales records (tax invoices and notes) instead of using paper.
- Why It Matters: This step was like setting up the base of a building. It made sure everyone was ready for more advanced steps in the future.
Phase 2: Elevating the Game (Integration Phase)
- Implementation: Done in stages, like a relay race where different businesses take part at different times based on their size.
Requirements for Businesses:
- They must fill out tax invoices with some extra details that are required.
- They need to use a special computer program for making these invoices, which is approved and connected to the tax system.
- These invoices should be in a special format (XML or PDF with XML).
- They need to send these invoices to a special tax platform (FATOORA) to get them checked and approved.
- Once approved, these invoices get a special digital stamp and QR code.
Stages of Phase 2 (Waves):
Wave 1:
- For Big Businesses: Those earning more than SAR 3 billion.
- Start Date: January 1, 2023.
- Adjustment Time: 6 months, from January to June 2023.
Wave 2:
- For Quite Big Businesses: Earning between SAR 500 million and SAR 3 billion.
- Start Date: July 1, 2023.
- Adjustment Time: 6 months, from July to December 2023.
Wave 3:
- For Large Businesses: Earning between SAR 250 million and SAR 500 million.
- Start Date: October 1, 2023.
- Adjustment Time: 4 months, from October 2023 to January 2024.
Wave 4:
- For Medium to Large Businesses: Earning between SAR 150 million and SAR 250 million.
- Start Date: November 1, 2023.
- Adjustment Time: 4 months, from November 2023 to February 2024.
Wave 5:
- For Medium Businesses: Earning between SAR 100 million and SAR 150 million.
- Start Date: December 1, 2023.
- Adjustment Time: 4 months, from December 2023 to March 2024.
Wave 6:
- For Smaller Medium Businesses: Earning between SAR 70 million and SAR 100 million.
- Start Date: January 1, 2024.
- Adjustment Time: 4 months, from January to April 2024.
Wave 7:
- For Smaller Businesses: Earning between SAR 50 million and SAR 70 million.
- Start Date: February 1, 2024.
- Adjustment Time: 4 months, from February to May 2024.
Wave 8:
- For Even Smaller Businesses: Earning between SAR 40 million and SAR 50 million.
- Start Date: February 1, 2024.
Each wave specifies which businesses are affected, based on their annual VAT turnover. The waves have different start dates and periods during which businesses must integrate the E-Invoicing system. This staggered approach allows for a smoother transition and accommodates businesses of various sizes.
Understanding Integration with ZATCA:
Many business people find the process of integrating their invoicing systems with ZATCA's platform (called FATOORA) a bit tricky. There's confusion about how to do it and which software to use. But don't worry, it's manageable once you know the steps.
Steps to Integrate with FATOORA Portal:
Log into FATOORA:
Go to the FATOORA portal website.
Use your ERAD credentials to log in.
Request OTP Codes:
Once logged in, ask for OTP (One-Time Password) codes. These codes are needed to connect your invoicing software to FATOORA.
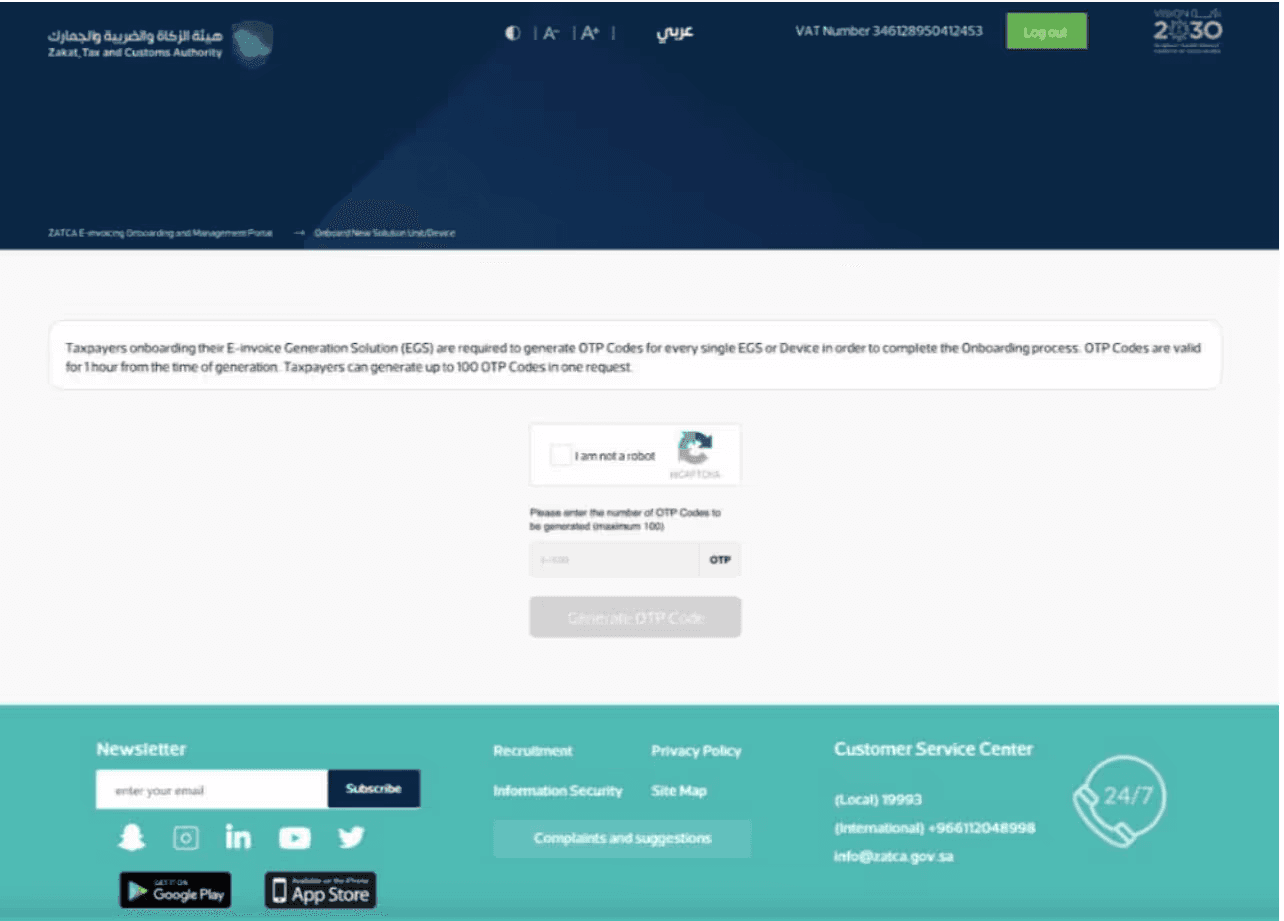
Enter OTP Codes:
Put these OTP codes into your E-Invoice Software (the program you use for creating electronic invoices).
Check if Successful:
After entering the OTP codes, check to see if your software has successfully connected (on-boarded) to FATOORA.
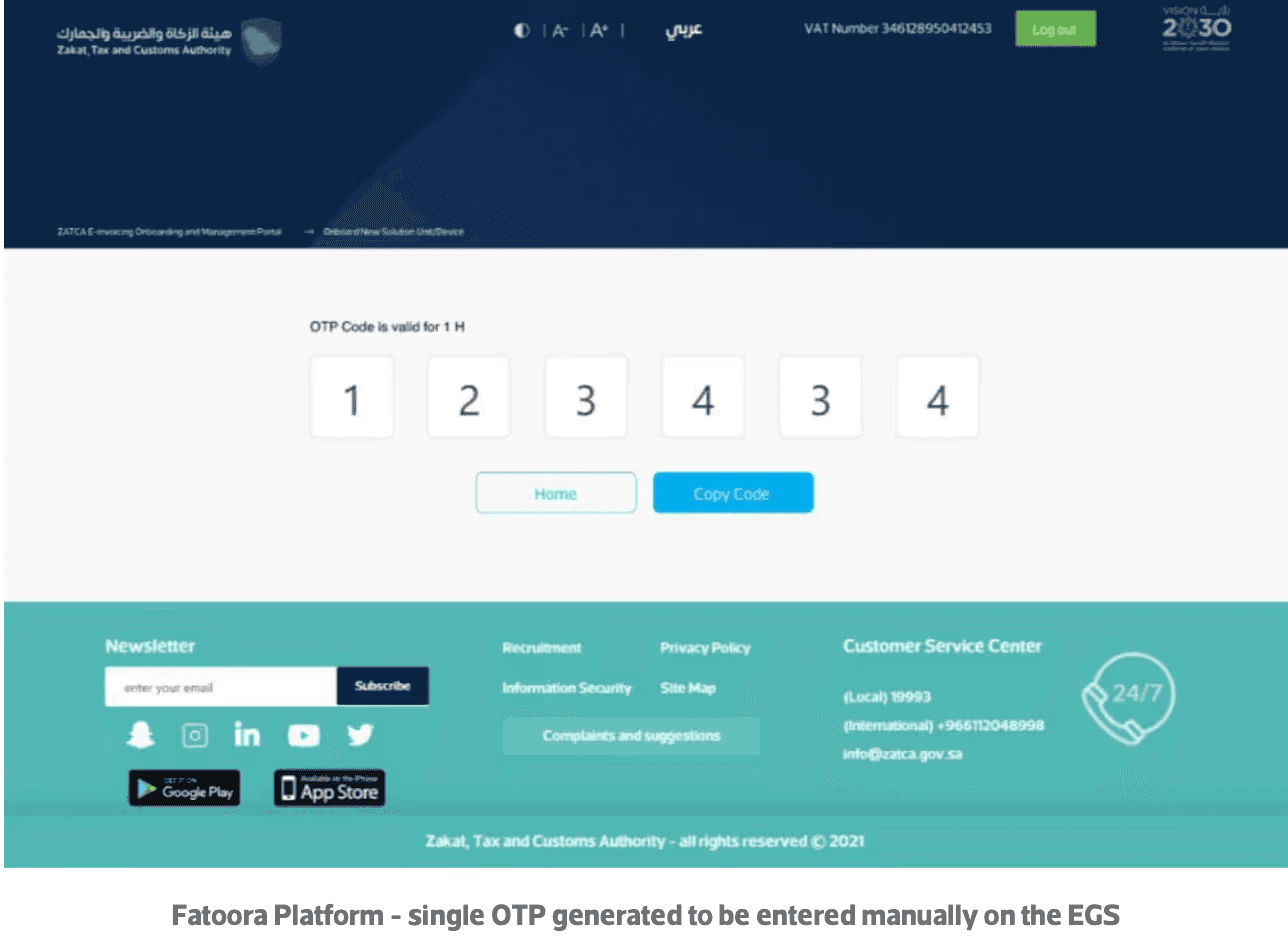
Helpful Tip:
💡 If you're looking for a good software solution to help with E-Invoicing and integration with ZATCA, consider checking out complyance They are known as one of the leading providers for Zatca E-invoicing solutions.
Why Pick Complyance: Simple Reasons They Stand Out
In today’s fast business world, following government rules is super important. For businesses in Saudi Arabia, sticking to ZATCA e-invoicing rules is a must. Among many companies offering this service, Complyance is a top choice. Here's why in simple terms:
- All About ZATCA E-Invoicing: Complyance focuses only on ZATCA e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia. This means they really understand the special needs and problems businesses there face. They make solutions just right for these needs.
- Always There When You Need It: Complyance works 99.9% of the time. This is great because businesses can count on them to be there all the time, with no breaks in sending out invoices.
- Good Prices, No Surprises: They offer services at prices that make sense and don’t hide extra costs. This means businesses know what they’re paying for without worrying about unexpected charges.
- Easy to Start Using: Complyance system can quickly fit into a business's existing setup. This means businesses can start using it fast, without losing time or money.
- Helpful Customer Support: They have a support team that’s always ready to help. Customers are happy with the quick and useful answers they get.
- Always Up-to-Date: Complyance.io keeps updating its software to match new ZATCA rules. This means businesses don’t have to worry about keeping up with the changes themselves.
- Safe and Rule-Following: They take protecting their clients' private info very seriously. Their system has strong safety features that meet top standards. This gives businesses peace of mind.
In simple words, Complyance is like a reliable and smart friend for businesses dealing with e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia. They make things easier, safer, and more efficient.
Discover More About Complyance
Interested in learning more about the Complyance platform? Their website is packed with detailed information that can help you understand their services better.
- Explore Their Website: Visit Complyance for in-depth insights. You can find out how their platform works, what makes it unique, and how it can benefit your business.
- Dive into Their APIs: If you're tech-savvy or want to know about the technical aspects, their website offers a section to explore the APIs. This is great for understanding how Complyance integrates with your existing systems.
- Request a Demo: Not sure if Complyance is right for you? Why not see it in action? You can request a demo at Complyance Demo Request. It's a great way to get a feel for the platform and see how it meets your needs.
- Read Their Blogs: Complyance has a collection of blogs related to ZATCA and e-invoicing at Complyance Blogs. These articles can provide you with additional insights, tips, and updates.
Take the time to explore and learn more. Complyance might just be the solution you're looking for!
Related posts
Frequently Asked Questions
ZATCA E-Invoicing is a system implemented in Saudi Arabia, requiring businesses to generate and process invoices electronically to ensure transparency and compliance with tax regulations.
All taxable persons and entities conducting business in Saudi Arabia are required to comply with ZATCA E-Invoicing requirements.
There are two main phases: Phase 1 focuses on generating and storing electronic invoices, and Phase 2 involves integration with ZATCA’s system for clearance and reporting.
Electronic invoices must be in XML format or PDF/A-3 with embedded XML, as per ZATCA guidelines.
Yes, businesses need to use an E-Invoice Generation Solution (EGS) that complies with ZATCA’s technical standards.
A standard tax invoice is used for business-to-business transactions, while a simplified tax invoice is used for transactions under SAR 1,000, often in business-to-consumer dealings.
It's a digital stamp added to electronic invoices and notes to verify their authenticity and the identity of the issuer.
Yes, ZATCA has set specific deadlines for businesses to comply, divided into waves based on their VAT turnover.
Non-compliance can lead to penalties, legal actions, and other consequences as per Saudi Arabian law.
You can visit ZATCA’s official website or consult with a service provider like Complyance for detailed guidelines and support.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get the latest compliance updates, e-invoicing news, and expert tips delivered to your inbox.
ABOUT COMPLYANCE
Empowering businesses to automate e-invoicing and stay compliant in 100+ countries. Our platform simplifies regulatory complexity for enterprises and fast-growing companies.
Go Live in a Week with Developer-Friendly Global E-Invoicing Platform
Complyance makes it easy for your IT/dev team to integrate once and automate E-Invoicing across 100+ countries. Built for fast deployment, field-level validation, and indirect tax accuracy—no delays, no rework.



