How Retail Companies in the UAE Can Simplify E-Invoicing with Complyance
Discover how Complyance’s e-invoicing software enables UAE retailers to stay e-invoicing compliant, automate invoice validation, and simplify multiple ERP, POS, and accounting systems integrations.

Table of Contents
Retail businesses in the UAE operate in a fast-moving environment where thousands of invoices are generated every day across multiple outlets, brands, and customer types. Behind every transaction lies a web of interconnected systems, from ERP to POS systems, that must stay perfectly aligned for operations to run smoothly.
With the UAE’s upcoming e-invoicing mandate, this ecosystem now needs to handle more than just transactions. Every invoice must be validated, structured, and transmitted through an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) in real time, following the Federal Tax Authority’s Peppol-based PINT AE standard.
For retailers, the goal is clear: stay UAE e-invoicing compliant without disrupting day-to-day operations. Yet achieving that can be challenging when each outlet uses a different POS, each entity relies on a different ERP, and transactions range from B2C counter sales to B2B corporate billing.
This is where the gap lies. Retailers need an e-invoicing solution that connects their various systems seamlessly, ensures every transaction meets the new e-invoicing requirements, and does all of this in real time without causing operational disruption.
Complyance fills that gap. It acts as your bridge to the UAE’s e-invoicing network. It enables seamless integration across every ERP and POS platform through a single unified API. With automated data mapping, real-time validation, and submission, retailers can ensure every B2B and B2G invoice meets FTA E-invoicing standards while continuing business as usualand also stay fully prepared for the upcoming B2C e-invoicing mandate when it comes into effect.
What is E-Invoicing and why does it really matter in the UAE
What Is E-Invoicing?
E-invoicing, also known as electronic invoicing, is the process of creating and exchanging invoices in a structured digital format that computers can read and validate automatically. Instead of sending a PDF or printed invoice, businesses submit these digital invoices through approved platforms like Complyance, where they are validated and shared with both the buyer and the government for compliance and reporting.
Why the UAE Is Making E-Invoicing Mandatory
Traditional VAT reporting reveals business transactions only after weeks or months have passed, creating blind spots in compliance and economic oversight.E-invoicing solves this by giving tax authorities real-time access to transactional data, enabling faster decisions, stronger enforcement, and greater transparency.
Here's what it enables:
- Combat Tax Fraud and Evasion: E-invoicing helps stop fake or duplicate invoices by checking them instantly when they’re created.
- Enable Real-Time VAT Reporting: Invoices are shared with the tax authority as soon as they’re issued, no more delays in VAT reporting.
- Improve Transparency Across Supply Chains: Each invoice is tracked digitally, making it easier to keep records and solve payment or reporting issues.
- Align with Global Standards: Using the Peppol network and the UAE’s PINT-AE format allows smoother trade and tax compliance with other countries.
- Reduce Administrative Burden: Automated invoicing cuts down manual work, saving time and reducing mistakes for businesses and tax teams
For more detailed information, read our blog: E-Invoicing in the UAE: Why It’s Mandatory for Businesses
Challenges Faced by Retail Industries in the UAE for E-Invoicing
1. Managing E-Invoicing Across Multiple Outlets and Legal Entities
Retail chains typically operate across several business units, branches, and trade licenses, each with its own tax registration. Coordinating e-invoicing readiness across these entities means ensuring consistent data flow, validation, and transmission from every location. Without centralized visibility, e-invoicing compliance tracking becomes difficult.
2. Integration Challenges with Multiple ERP & POS Systems
Retailers use a mix of systems from SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics to custom-built POS solutions. However, these platforms are not natively Peppol-compliant. They can’t directly generate or transmit structured XML invoices to the FTA. Bridging that gap requires an API layer that can interpret, validate, and reformat invoices automatically, something Complyance was built to handle.
3. Segregating B2B and B2C Transactions
Not every transaction needs to be reported the same way. While B2B and B2G invoices are mandatory and must go through real-time validation and submission, B2C receipts are currently exempt from e-invoicing in UAE but must still be traceable. For retailers with hybrid operations, this creates a challenge: it’s difficult to distinguish and route invoices based on transaction type. While B2C is not yet mandatory, industries must be prepared for future updates where even B2C invoices may require similar validation, making it essential for retailers to ensure their systems can adapt as regulations evolve.
4. Ensuring Validation and Error-Free Submission
Every e-invoice must pass FTA validation checks before approval. Even a single missing field or incorrect tax code can lead to rejection. When thousands of invoices flow daily, manually fixing validation errors isn’t sustainable, and delays can result in UAE e-invoicing penalties or disrupted reporting.
5. Adapting to the Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) Model
Under the UAE’s DCTCE (Decentralized Continuous Transaction Control and Exchange) model, invoices can no longer be simply generated and stored. They must be validated in real-time via an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) before being sent to the customer. Retailers must ensure that their systems can process invoices quickly and accurately while adhering to the strict e-invoicing requirements of the UAE. This can be challenging due to the complexity of managing large volumes of transactions across multiple systems, maintaining data accuracy, and addressing potential integration issues as systems evolve or face technical disruptions, which can delay invoice processing and submission.
6. Keeping Up with Phased Implementation Deadlines
The e-invoicing rollout is phased between July 2026 and March 2027, depending on company size. Since the mandate will begin with large enterprises, these retailers must be prepared to process large volumes of invoices across multiple outlets, with complex integrations between ERPs and POS systems. Retailers with large-scale operations need to start early to ensure that all systems are connected, tested, and validated well before the enforcement deadline, allowing ample time to handle the scale of transactions and avoid last-minute disruptions.
How Complyance Simplifies E-Invoicing for Retailers
Complyance goes beyond integration support; it brings every aspect of e-invoicing into one intelligent, automated environment. For retailers dealing with multiple outlets, thousands of daily transactions, and constant system updates, Complyance ensures that compliance never slows down operations.
1. One API for Global E-Invoicing
Complyance provides a single API that connects all your systems to global e-invoicing Platform. Whether your business operates in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, or other Peppol-enabled regions, you can manage every country’s requirements through one connection. This reduces the need for multiple vendor integrations and enables faster rollouts across new markets.
2. Auto Mapping
From data extraction to automated mapping, real-time validation, and submission, the Complyance platform ensures that every B2B and B2G invoice adheres to the FTA’s PINT AE format, while automatically flagging missing or invalid fields before submission. This removes manual validation work and drastically reduces the chances of rejection.
3. Real-Time e-invoicing compliance and Visibility
Retailers can view every invoice journey from creation to successful submission in real time. Any failures or pending validations are highlighted instantly, helping your teams act quickly. With complete transparency, your business remains audit-ready at all times.
4. Seamless Integration Across All ERP, POS, and Accounting Systems
Complyance is designed to work across every ERP, POS, or custom billing system. Whether you’re running SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, or an in-house setup, Complyance connects effortlessly without requiring major system changes.
5. Continuous mandate Updates and Local Adaptation
As the UAE’s e-invoicing framework evolves, Complyance updates automatically. Retailers never have to worry about adjusting XML structures, tax field mappings, or submission logic. Every update is tested, deployed, and maintained on the platform, ensuring your e-invoicing workflows stay aligned with the latest FTA standards.
6. Bulk Upload Invoices in Real Time
Retailers can upload large volumes of invoices instantly using Excel batch uploads or connect directly through the API for real-time submission. This capability is ideal for high-volume retail environments where speed and accuracy are critical for UAE e-invoicing compliance.
7. Automatic PINT-AE Formatting
Complyance automatically formats every invoice to the PINT-AE standard, eliminating the need for manual mapping or data transformation. The system ensures every field, code, and structure aligns perfectly with FTA specifications.
8. Real-Time Error Fixes
The platform provides instant validation feedback, allowing retailers to detect and correct data issues before submission. This reduces rejections and ensures invoices are approved by the FTA without delay.
9. 24/7 Support and Sandbox Testing
Complyance offers round-the-clock technical and compliance support along with a dedicated sandbox testing environment. Retailers can validate their entire e-invoicing workflow before going live, ensuring smooth deployment and reliable performance.
Multiple ERPs, 10+ POS Systems, And Now Real-Time E-Invoicing?
Connect every outlet, ERP, and POS without disrupting operations — contact our team now.
How Complyance Simplifies API Integration for E-Invoicing in Retail Industries Using Multiple ERPs and POS
Use Case 1: Centralized Database for Multiple ERPs and POS Systems
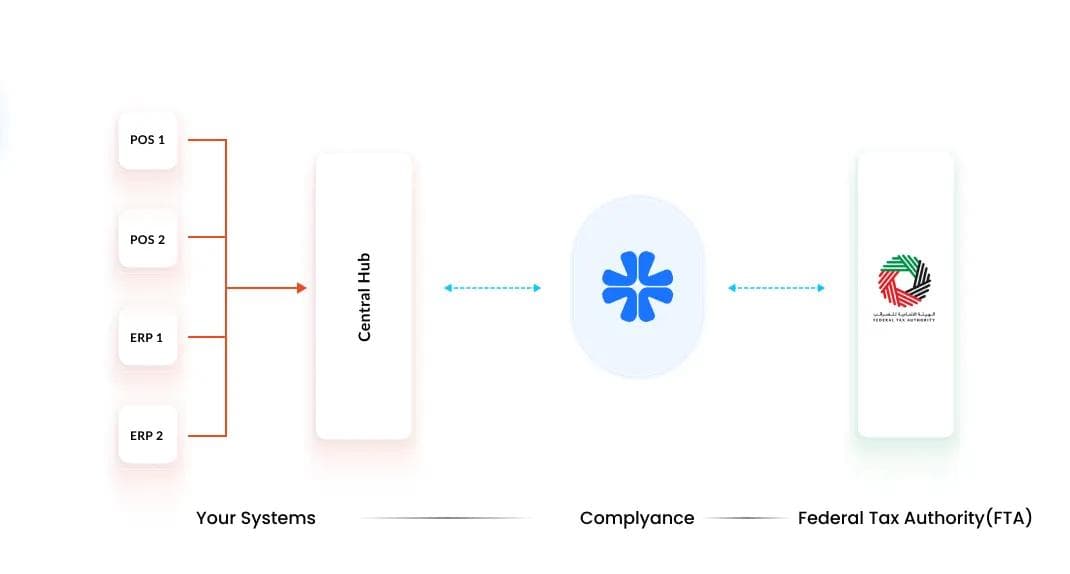
Overview
Large retail enterprises often operate across multiple outlets, brands, and business units, each using different ERP and POS systems. This creates complexity when integrating e-invoicing across the organization.By establishing a centralized database system or Central Hub, retailers can simplify how data from various ERPs and POS systems is segregated and made available for e-invoicing.
Integration Approach
In this setup, all transactional data from multiple ERPs and POS systems is stored centrally in a unified database.Complyance connects directly to this central database, pulling the invoice data through sdk for automated mapping, real-time validation, and submission to the FTA’s e-invoicing network.This ensures a single source of truth for all e-invoicing transactions across the enterprise.
Process Flow
- Data segregation: All ERPs and POS systems feed their invoice data into the central database.
- Data Extraction: Complyance retrieves the segregation data from the central database.
- Mapping & Validation: The platform automatically maps invoice field headers to the FTA’s PINT AE schema and performs validation checks.
- Submission: Validated invoices are submitted in real time to the FTA via Complyance’s accredited infrastructure.
- Monitoring: Every transaction’s status can be tracked from the centralized dashboard.
Outcome
- Faster Go-Live: Integration is completed quickly since data comes from a single, unified source.
- High Accuracy: Centralized data minimizes mismatches or duplication.
- Simplified Maintenance: Changes or updates in the schema or format only need to be applied once at the central level.
- Unified Compliance Monitoring: Your team can view all outlets and entities through a single e-invoicing dashboard.
Advantages
- Centralized control of all invoice data.
- Reduced integration complexity.
- Faster deployment and easier scalability.
- Minimal manual intervention.
- Consistent and standardized data across all ERPs and POS systems.
Disadvantages
- Requires upfront setup of a central database if one doesn’t exist.
- Data synchronization between individual systems and the database must be maintained continuously.
- If the central database faces downtime, it can temporarily affect invoice submission.
Which industries would be suited for?
Retail enterprises, large retail SaaS platforms, and multi-brand retail groups operating with central ERP and POS data systems.
Summary
The centralized database approach is the most efficient integration model for large enterprises managing multiple ERPs and POS systems.It simplifies the e-invoicing journey by offering centralized control, faster go-live, and real-time e-invoicing visibility, making it the recommended architecture for large-scale retail environments.
Use Case 2: Multiple ERPs and POS Without a Central Database
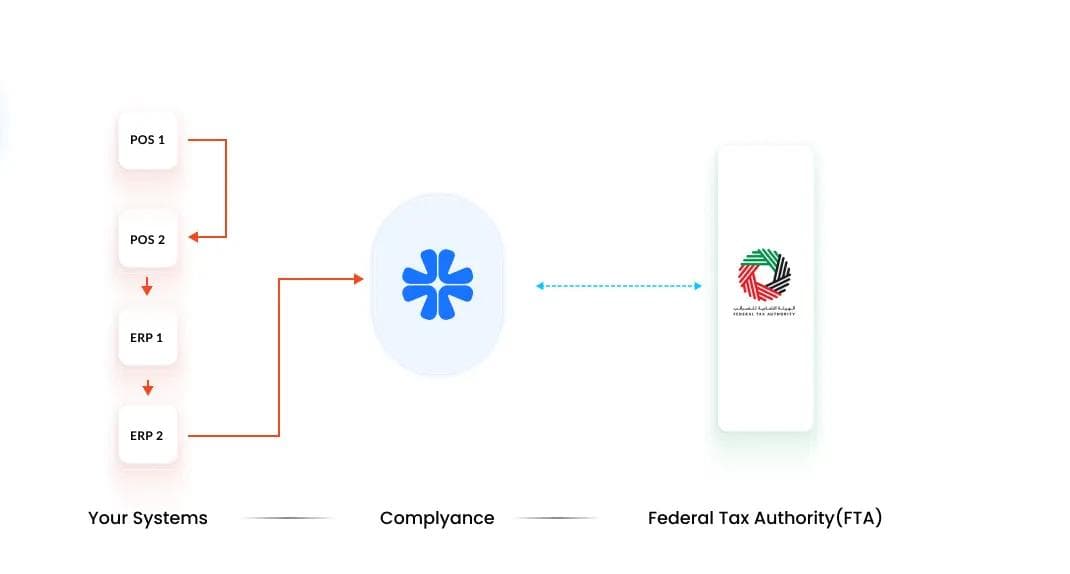
Overview
Some retail enterprises operate with multiple ERPs and POS systems but do not maintain a centralized database. In such cases, the data flow becomes more fragmented, as each ERP and POS works independently.This structure can create integration challenges when implementing e-invoicing across multiple systems, as data must be collected and standardized before submission to the FTA.
Integration Approach
In this setup, POS data is transmitted to the respective ERPs, and from there, the data is pushed through the SDK to the Complyance platform for validation and e-invoicing. Each ERP–POS connection is managed separately, ensuring that invoice data from every system is processed accurately and in compliance with the UAE’s e-invoicing framework.
Process Flow
- POS Data Transmission: Each POS system sends its invoice data to the ERP it is connected. In many retail environments, multiple POS systems feed their data into a single ERP, which then consolidates and forwards the processed data to another ERP at the group level. From there, the data is pushed through the SDK to the Complyance platform for validation and e-invoicing submission.
- ERP Data Push: The ERP then pushes the processed invoice data through the SDK to Complyance.
- Mapping and Validation: Complyance automatically maps the data fields to the FTA’s PINT AE schema and validates each invoice.
- Submission: Validated invoices are submitted in real time to the FTA.
- Monitoring: Each ERP–POS connection can be monitored individually for validation success and compliance status.
Outcome
- Smooth Multi-System Integration: Each ERP and POS is integrated independently while maintaining compliance across all systems.
- Data Consistency: Automated validation ensures that invoice formats and tax fields remain accurate across varied systems.
- Real-Time Compliance: Retailers can still achieve real-time validation and submission even without a central database.
Advantages
- Allows integration without major restructuring of existing systems.
- Complyance handles data from multiple ERPs and POS setups simultaneously.
- Real-time processing through SDK ensures compliance continuity.
- Suitable for businesses that haven’t yet migrated to centralized data architecture.
Disadvantages
- Higher integration complexity due to multiple independent connections.
- Slightly longer setup time compared to centralized database integration.
- Data consistency depends on how effectively ERPs receive and process data from different POS systems.
- Maintenance can become more demanding as new systems are added.
Which industries would be suited for?
Retail groups with distributed systems, franchise-based retail chains, and multi-entity enterprises manage separate ERPs for different business units.
Summary
The multiple ERPs and POS without a central database model provide a flexible integration path for retailers that are still transitioning toward unified data systems.While it requires separate connections for each ERP and POS combination, Complyance simplifies the entire process through SDK-driven automation, ensuring every invoice is validated, formatted, and submitted accurately in real time.
Use Case 3: Clustering POS Systems
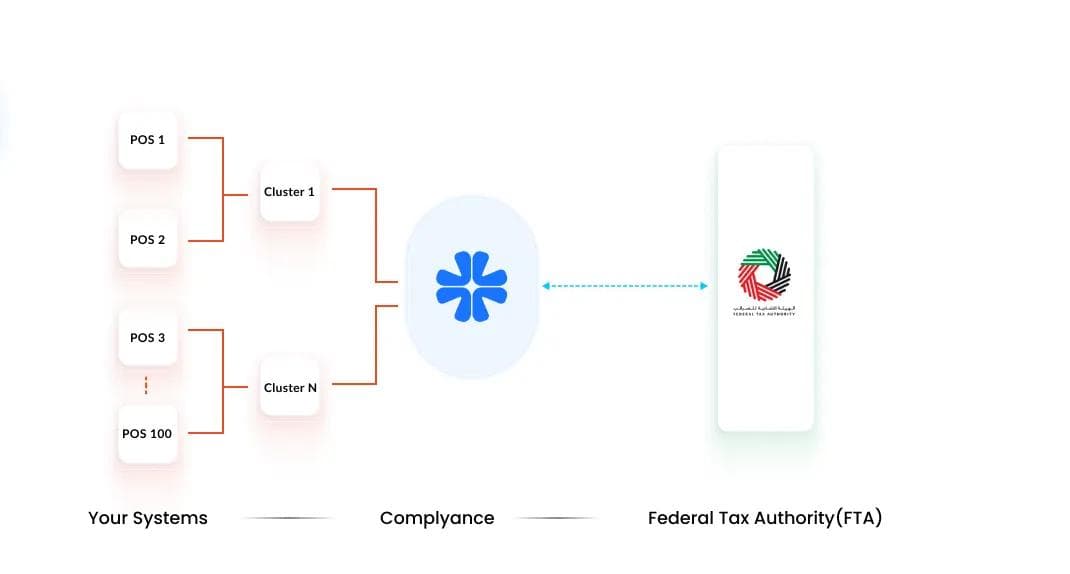
Overview
Retailers with many outlets often operate multiple POS systems across regions or business units. Managing integration for every POS system individually can be complex and time-consuming.To simplify this, many organizations cluster their POS systems into groups, allowing them to manage and process data in smaller, more structured batches.
Integration Approach
In this setup, POS systems are grouped into clusters by the organization, for example, by region, brand, or business unit.Complyance integrates with each cluster to process the data in batches, ensuring every transaction is mapped, validated, and submitted according to FTA requirements.This approach reduces data congestion and simplifies how large-scale retail networks handle e-invoicing integration.
Process Flow
- POS Clustering: The organization groups multiple POS systems into clusters based on operational logic (e.g., store type, location, or ERP linkage).
- Data Collection: Each cluster transmits its consolidated data for processing.
- Integration with Complyance: Complyance connects to each cluster to validate and map invoice data.
- Validation and Mapping: Data from each cluster is automatically aligned with the FTA’s PINT AE schema.
- Submission: Validated invoices are sent to the FTA through Complyance’s platform, with results tracked in real time.
Outcome
- Streamlined Data Management: Processing data in clusters helps retailers handle large volumes of invoices more efficiently.
- Faster Integration: Clustering minimizes the number of direct integrations needed and speeds up go-live timelines.
- Reduced Bottlenecks: Data from each cluster is processed in manageable batches, preventing overload or submission delays.
Advantages
- Simplifies the management of multiple POS systems.
- Improves performance and reduces load on individual systems.
- Enables parallel processing of invoice data from different clusters.
- Easier monitoring and troubleshooting for large retail networks.
Disadvantages
- Requires internal coordination to establish and maintain clusters.
- Cluster-level data synchronization must be managed to avoid inconsistencies.
- May still require ERP-level alignment if clusters feed into different back-end systems.
Which industries would be suited for?
Retail enterprises with multiple outlet-level POS systems, supermarket and hypermarket chains, and quick-service retail operations that process high daily transaction volumes
Summary
The POS clustering model offers retailers an efficient way to manage large volumes of transactional data across many outlets. By grouping POS systems into clusters and integrating them with Complyance, businesses can achieve faster validation, streamlined reporting, and reduced operational load — making it an effective approach for large retail chains preparing for e-invoicing compliance.
Use Case 4: Multiple ERPs Without a Central Database
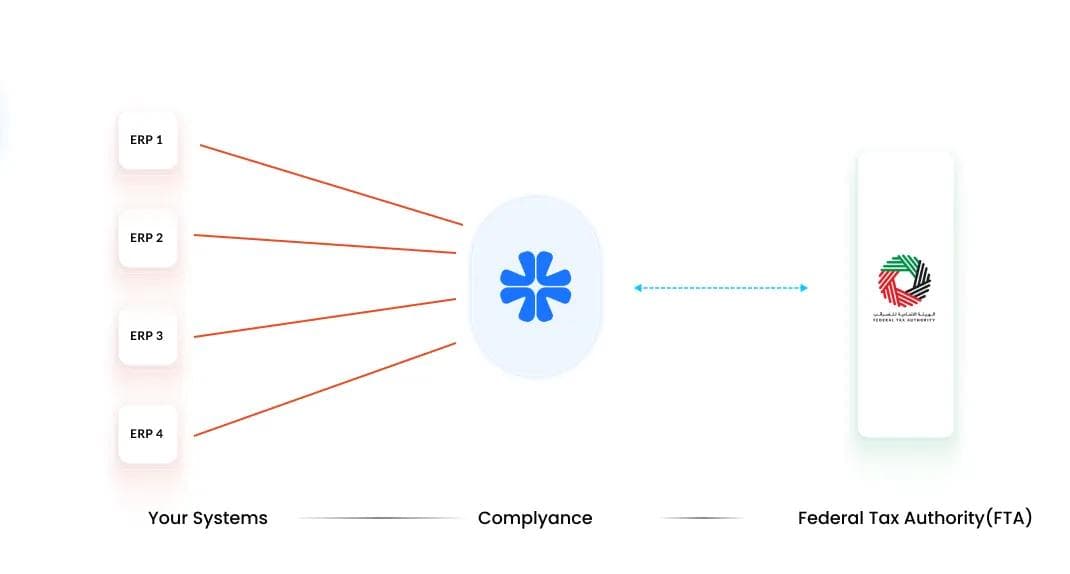
Overview
Some retail enterprises operate with multiple ERP systems but without a central database to unify their data. Each ERP may function independently for different business units, regions, or product categories. This decentralized setup makes e-invoicing more complex, as invoice data must be validated and submitted separately from each ERP system while maintaining consistency across the organization.
Integration Approach
In this model, each ERP system is integrated via API with the Complyance platform, where the data is processed for e-invoicing. Complyance manages the mapping, validation, and submission workflow for every ERP connection individually. This ensures that invoices from each ERP system comply with the UAE’s DCTCE framework and are transmitted securely to the FTA.
Process Flow
- Data Extraction: Each ERP system prepares its invoice data for e-invoicing.
- API Integration: Invoice data from each ERP is sent to Complyance through secure API endpoints.
- Mapping and Validation: Complyance automatically maps and validates the data according to the FTA’s PINT AE schema.
- Submission: Validated invoices are submitted in real time to the FTA.
- Monitoring: Each ERP’s transaction flow is tracked independently within the Complyance dashboard.
Outcome
- Independent ERP Integration: Each ERP system connects directly to Complyance through APIs, maintaining full compliance across all entities.
- Automated Validation: Complyance handles schema mapping and validation automatically for every ERP.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures all invoices meet UAE’s e-invoicing standards, even without a centralized data structure.
Advantages
- No need for central data restructuring or major architectural changes.
- Enables retailers with multiple ERP systems to become compliant quickly.
- Supports gradual, phased integration for each ERP.
- Provides flexibility to scale or modify ERP systems independently.
Disadvantages
- Integration and validation must be performed for each ERP separately, which can extend go-live timelines.
- Invoices from different ERPs may require additional reconciliation efforts.
- More maintenance is required compared to a centralized or clustered data setup.
- Integration burnout will happen during e-invoicing implementation.
Which industries would be suited for?
Enterprises using different ERPs across subsidiaries, diversified retail brands, and retail SaaS companies are managing separate ERP environments for clients.
Summary
The multiple ERPs without a database model are best suited for retailers who operate diverse systems across entities but lack centralized infrastructure. By connecting each ERP directly via API, Complyance ensures every invoice is validated, mapped, and submitted in real time, providing a robust and scalable path to compliance even in distributed environments.
Implementation: How Retailers Can Integrate Their ERP with the Complyance API
Once retailers finalize their preferred integration model, the next step is to connect their ERP or POS systems with the Complyance API. The setup is simple, developer-friendly, and designed to help large retail environments go live quickly without requiring extensive technical work.
Step 1: Get Started with the Integration Panel
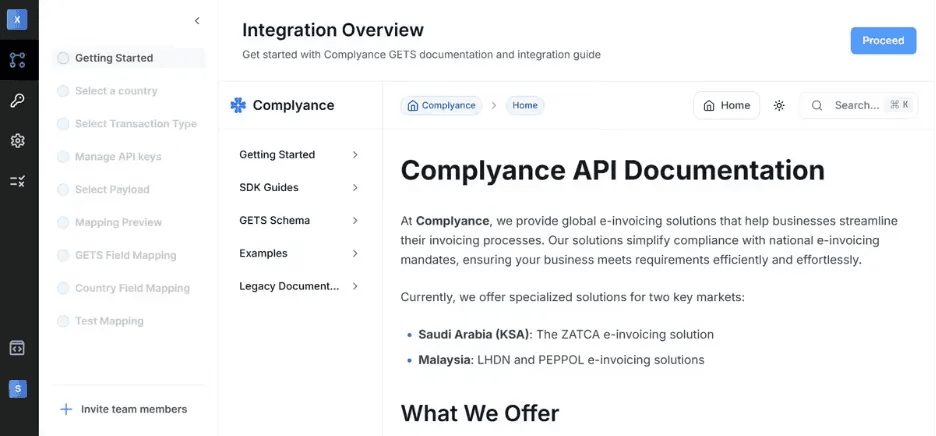
Once you log into the Complyance platform, you’ll see a navigation sidebar on the left. From here: Expand the Developer Portal section at the bottom. You’ll find two options under Portals:
- Invoice Portal
- Developer Portal
Click on Developer Portal to access the Integration Engine, where you’ll land on the Integration Overview screen. This is your starting point to access:
- SDK Guides – Step-by-step instructions for setting up and using Complyance SDKs.
- GETS Schema Documentation – Detailed breakdown of standard fields and country-specific mappings.
- Example Payloads – Sample JSON structures and response formats to help align your ERP output.
- Legacy Docs – Useful for teams migrating from older invoice formats or systems.
This section gives your developers everything they need to get started, from understanding GETS to pushing validated data using SDKs. On the left sidebar, you’ll also find a progress-driven checklist, starting from country selection and ending with test mapping, making it easy to track integration progress from start to finish.
Java SDK Setup (Recommended Path for Developers)
Complyance currently supports a Java SDK for production-grade integration with ERP or billing systems. In upcoming updates, SDKs for C++, JavaScript (Node.js), and Python will also be available to support a wider range of technology stacks. For now, if you’re using Java, follow the steps below:
Installation: Java SDK Setup We recommend using the automated setup, which detects your operating system and generates the correct configuration path for you.
macOS & Linux Setup
Install Java (JDK 11 or higher)
brew install openjdk@11Set the JAVA_HOME environment variable
export JAVA_HOME=$(/usr/libexec/java_home -v 11) Verify Java Installation
java –version- pic Windows:
- Download and install OpenJDK 11+
- Set the JAVA_HOME environment variable
- Add Java to PATH
After setting up the Installation, go to the Developer portal and start implementing it
Step 2: Mapping and Testing
Once your SDK is connected, proceed through the Integration Checklist:
- Select Country – Choose the country (for example, UAE).
- Select Transaction/invoice Type – Choose the invoice type (Tax Invoice, Credit Note, or Debit Note) and define whether the transaction is B2B, B2C, or B2G.
- Manage API Keys – Securely generate API credentials.
- Select Payload – Configure the data structure for your ERP invoices.
- Mapping Preview – Match your ERP field headers with Complyance’s GETS schema.
- Country Field Mapping – Apply country-specific validation rules (for example, PINT AE for UAE).
- Test Mapping – Run validation tests before going live.
Once testing is complete, you can move to live mode, where invoices are processed, validated, and submitted in real time through Complyance platform.
Step 3: Go Live
After successful testing, your integration is ready for production. Retailers can begin submitting live invoices from their ERP or POS systems to the FTA via Complyance. The platform monitors each transaction in real time and provides status visibility for every invoice submitted, ensuring no data is lost or delayed.
For a more detailed and full implementation process, read our blog: How to Implement UAE E-Invoicing with the Complyance API Platform: A Step-by-Step Guide
Option B: Excel Upload (Easiest way for doing E-Invoicing)
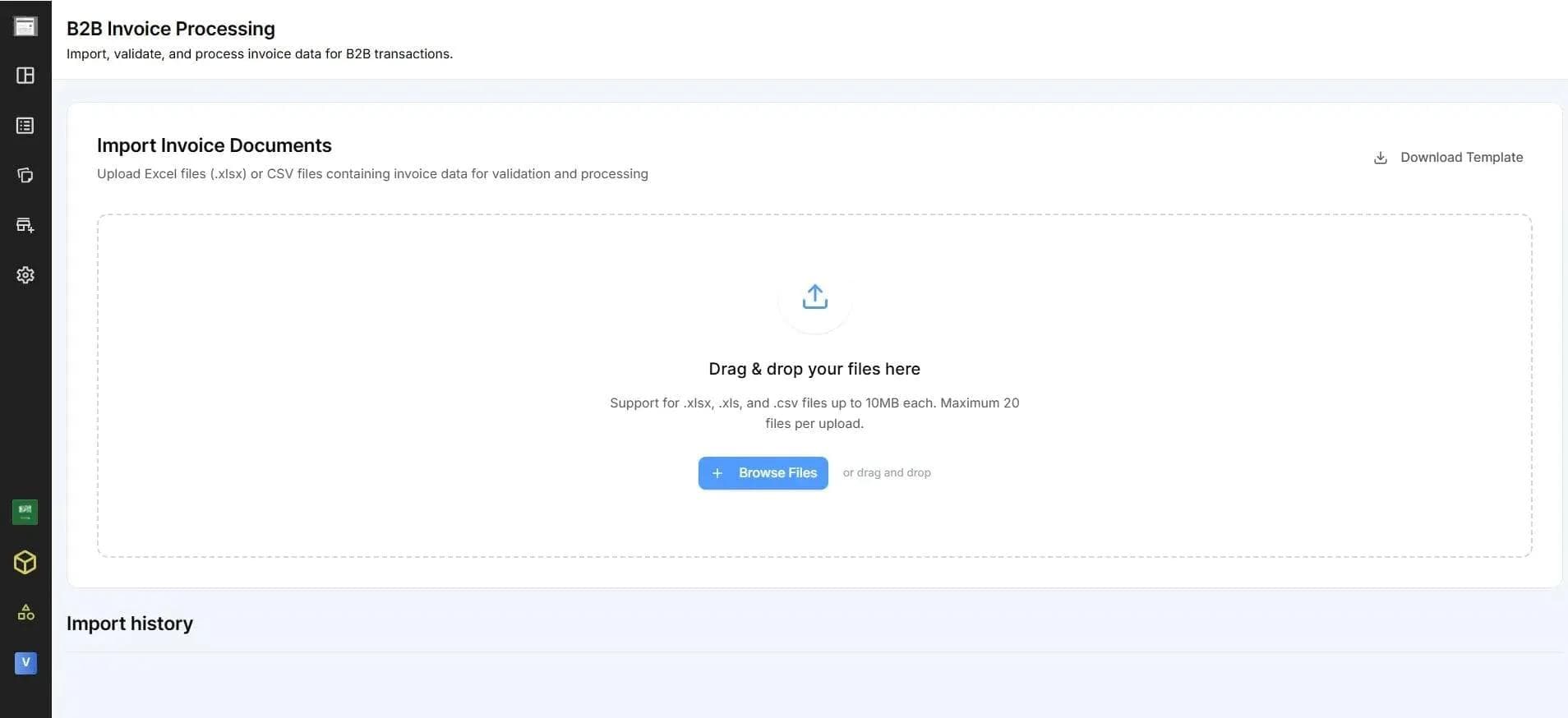
For the teams that already manage invoices in spreadsheets, the Excel Upload option offers a convenient way to process many invoices at once.Here’s the process:
- Download the pre-formatted Excel template from your Complyance dashboard
- Fill in all invoice rows with the required details
- Upload the completed sheet back to the platform
- Complyance auto-validates each entry, showing clear errors (like missing TRNs or VAT mismatches)
Bonus: Smart dropdowns and data validation in the template help reduce manual mistakes while preparing the sheet.
Bonus Features for Retail Finance Teams
Complyance doesn’t just simplify integration; it also equips finance teams with advanced tools to manage and monitor UAE e-invoicing more efficiently. These features help streamline day-to-day financial operations, reduce manual tracking, and maintain complete visibility across every outlet and entity.
1. Downloadable XML and Signed PDFs
Finance teams can easily download both FTA-validated XML files and digitally signed PDF versions of invoices directly from the Complyance dashboard. This ensures secure storage, easy access during audits, and complete traceability for every transaction.
2. Outlet-Level Reporting and Invoice Breakdowns
Gain detailed insights into outlet-level performance, with granular reporting that breaks down invoices by outlet, branch, or business unit. This gives retail enterprises the visibility needed to track volumes and measure e-invoicing readiness across locations.
3. VAT Mismatch Alerts and Duplicate Detection
Complyance’s e-invoicing software automatically scans and flags any VAT mismatches, missing fields, or duplicate invoices in real time. Retailers receive instant alerts, allowing finance teams to address issues before submission and avoid costly penalties.
4. Integration with third-party Systems
Complyance easily integrates with popular accounting platforms such as Tally, Zoho Books, QuickBooks, and Xero, ensuring smooth synchronization between e-invoicing workflows and financial reporting systems. This helps retail companies in the UAE maintain a single source of truth across tax and accounting operations.
Why Retailers Choose Complyance Over Other Providers
Benefits of e-invoicing if retail businesses choose Complyance:
- Faster Go-Live: Retailers can connect and begin e-invoicing in weeks instead of months.
- Reduced technical Dependence: The platform handles all validation and mapping, freeing internal teams from heavy technical involvement.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated data validation eliminates field errors and schema mismatches before submission.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce manual workloads, ensuring smoother invoice handling across outlets.
- Future-Proof e-invoicing: One API keeps you ready for future GCC and international e-invoicing mandates.
- Centralized Control: Gain complete visibility over e-invoicing status, transaction volumes, and outlet-level performance from one dashboard.
- Scalable Integration: Whether you expand to new regions or add new ERP/POS systems, Complyance scales instantly without re-engineering your setup.
- Developer-Ready, Finance-Friendly: Built for both tech and finance teams, Complyance makes API integration simple for developers while giving finance users full visibility, reporting, and control.
Final Tips for UAE Retailers Preparing for the e-invoicing Mandate
1. Centralize Multi-Outlet e-invoicing Under One Workspace
Bring all your outlets, branches, and legal entities under one unified e-invoicing solution. Complyance enables centralized compliance management, allowing teams to monitor every outlet’s e-invoicing status in real time from a single dashboard.
2. Clean Up POS/ERP Data
Verify and standardize critical data such as TRNs, VAT codes, and customer information across all systems. Clean data ensures successful validation and faster go-live.
3. Train Internal Teams
Ensure that your internal teams are familiar with the e-invoicing workflow, from data entry to validation and submission. Well-trained teams help prevent last-minute disruptions and maintain consistency across all operations.
4. Start Early with Sandbox Testing
Begin testing your e-invoicing software in a sandbox environment to identify data gaps, field mismatches, and validation errors early. This ensures a smoother transition when moving to live production.
Conclusion
E-invoicing for retail isn’t just about compliance; it’s about simplifying complexity. With multiple ERPs, POS systems, and large transaction volumes, retailers need a solution that works across every layer of their business. Complyance delivers that simplicity. It simplifies e-invoicing through automated mapping, real-time validation, and submission across all your systems, helping you go live faster and stay e-invoicing compliant without disrupting operations. With Complyance, retailers can turn e-invoicing into an advantage: faster processes, cleaner data, and seamless operations across every outlet and entity.
Related posts
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get the latest compliance updates, e-invoicing news, and expert tips delivered to your inbox.
ABOUT COMPLYANCE
Empowering businesses to automate e-invoicing and stay compliant in 100+ countries. Our platform simplifies regulatory complexity for enterprises and fast-growing companies.